Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMGNYIH)
| Drug Name |
Retigabine
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Ezogabine; Potiga; Trobalt; Retigabine [USAN]; D 20443; D 23129; ADD-230001; D-20443; D-23129; GKE-841; KE-0201; Ethyl 2-amino-4-((p-fluorobenzyl)amino)carbanilate; Ethyl N-[2-amino-4-[(4-fluorophenyl)methylamino]phenyl]carbamate; [2-Amino-4-[[(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]amino]phenyl]-carbamate; Ethyl N-(2-amino-4-(4-fluorobenzylamino)phenyl)carbamate hydrochloride; N-(2-Amino-4-(4-fluorobenzylamino)phenyl)carbamic acid ethyl ester; Ethyl (2-amino-4-(((4-fluorophenyl)methyl)amino)phenyl)carbamate; N-(2-Amino-4-(4-fluorobenzylamino)-phenyl) carbamic acid ethyl ester; Carbamic acid, (2-amino-4-(((4-fluorophenyl)methyl)amino)phenyl)-, ethyl ester
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Anticonvulsants
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Humans and other mammals
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
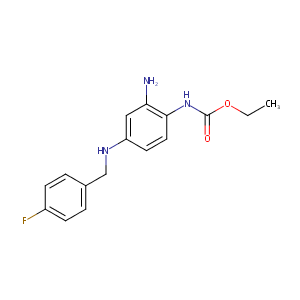 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 303.33 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 2.8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurposed Drugs (RPD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed RPD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Expression Atlas of This Drug
| The Studied Disease | Behcet disease | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICD Disease Classification | 4A62 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Expression Atlas (MEA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Retigabine (Comorbidity)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug Inactive Ingredient(s) (DIG) and Formulation(s) of This Drug
References
| 1 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of GlaxoSmithKline. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | Antibodies and venom peptides: new modalities for ion channels. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2019 May;18(5):339-357. | ||||
| 3 | Trend Analysis of a Database of Intravenous Pharmacokinetic Parameters in Humans for 1352 Drug Compounds | ||||
| 4 | The urinary safety profile and secondary renal effects of retigabine (ezogabine): a first-in-class antiepileptic drug that targets KCNQ (K(v)7) potassium channels. Epilepsia. 2012 Apr;53(4):606-12. | ||||
| 5 | Retigabine N-glucuronidation and its potential role in enterohepatic circulation. Drug Metab Dispos. 1999 May;27(5):605-12. | ||||
| 6 | N-Glucuronidation of the antiepileptic drug retigabine: results from studies with human volunteers, heterologously expressed human UGTs, human liver, kidney, and liver microsomal membranes of Crigler-Najjar type II. Metabolism. 2006 Jun;55(6):711-21. | ||||
| 7 | Modulation of the heart's electrical properties by the anticonvulsant drug retigabine. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2017 Aug 15;329:309-317. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2017.06.018. Epub 2017 Jun 20. | ||||
| 8 | The Sensorless Pore Module of Voltage-gated K+ Channel Family 7 Embodies the Target Site for the Anticonvulsant Retigabine. J Biol Chem. 2016 Feb 5;291(6):2931-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.683185. Epub 2015 Dec 1. | ||||
| 9 | The acrylamide (S)-1 differentially affects Kv7 (KCNQ) potassium channels. Neuropharmacology. 2006 Nov;51(6):1068-77. | ||||
| 10 | The SUMO-specific protease SENP2 plays an essential role in the regulation of Kv7.2 and Kv7.3 potassium channels. J Biol Chem. 2021 Oct;297(4):101183. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.101183. Epub 2021 Sep 10. | ||||
| 11 | Product Information. Fycompa (perampanel). Eisai Inc, Teaneck, NJ. | ||||
| 12 | Canadian Pharmacists Association. | ||||
| 13 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "UK Summary of Product Characteristics.". | ||||
| 14 | Iannini PB "Cardiotoxicity of macrolides, ketolides and fluoroquinolones that prolong the QTc interval." Expert Opin Drug Saf 1 (2002): 121-8. [PMID: 12904146] | ||||
| 15 | Product Information. Sirturo (bedaquiline). Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Titusville, NJ. | ||||
| 16 | Product Information. Arcapta Neohaler (indacaterol). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 17 | Product Information. Daurismo (glasdegib). Pfizer U.S. Pharmaceuticals Group, New York, NY. | ||||
| 18 | Bengtsson B, Fagerstrom PO "Extrapulmonary effects of terbutaline during prolonged administration." Clin Pharmacol Ther 31 (1982): 726-32. [PMID: 7042176] | ||||
| 19 | Belcastro V, Costa C, Striano P "Levetiracetam-associated hyponatremia." Seizure 17 (2008): 389-90. [PMID: 18584781] | ||||
| 20 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "Australian Product Information.". | ||||
| 21 | Product Information. Austedo (deutetrabenazine). Teva Pharmaceuticals USA, North Wales, PA. | ||||
| 22 | Product Information. Ingrezza (valbenazine). Neurocrine Biosciences, Inc., San Diego, CA. | ||||
| 23 | Product Information. Adcetris (brentuximab vedotin). Seattle Genetics Inc, Bothell, WA. | ||||
| 24 | Product Information. Rukobia (fostemsavir). ViiV Healthcare, Research Triangle Park, NC. | ||||
| 25 | Product Information. Xalkori (crizotinib). Pfizer U.S. Pharmaceuticals Group, New York, NY. | ||||
| 26 | Product Information. Tagrisso (osimertinib). Astra-Zeneca Pharmaceuticals, Wilmington, DE. | ||||
| 27 | Product Information. Retevmo (selpercatinib). Lilly, Eli and Company, Indianapolis, IN. | ||||
| 28 | Product Information. Braftovi (encorafenib). Array BioPharma Inc., Boulder, CO. | ||||
| 29 | Product Information. Zulresso (brexanolone). Sage Therapeutics, Inc., Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 30 | Product Information. Reyvow (lasmiditan). Lilly, Eli and Company, Indianapolis, IN. | ||||
| 31 | Product Information. Farydak (panobinostat). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 32 | Product Information. Zeposia (ozanimod). Celgene Corporation, Summit, NJ. | ||||
| 33 | Product Information. Nuplazid (pimavanserin). Accelis Pharma, East Windsor, NJ. | ||||
| 34 | Product Information. Macrilen (macimorelin). Aeterna Zentaris, Charleston, SC. | ||||
| 35 | Product Information. Barhemsys (amisulpride). Acacia Pharma, Inc, Indianapolis, IN. | ||||
| 36 | Product Information. Bevyxxa (betrixaban). Portola Pharmaceuticals, South San Francisco, CA. | ||||
